Describe Where Pyruvate Is Oxidized to Acetyl Coa
How is pyruvate oxidized to acetyl. Pyruvates carboxyl groups CO2 the remaining two carbon fragment is oxidized acetate becomes acetyl CoA.

Pyruvate Oxidation Biology For Majors I
This pathway will harvest the remainder of the extractable energy from what began as a glucose molecule and release the remaining four CO 2 molecules.

. The enzyme-bound acetyl group is transferred to CoA producing a molecule of acetyl CoA. Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl coa. Each pyruvate molecule loses a carboxylic group in the form of carbon dioxide.
Describe in general terms the two main stages of. The remaining two carbons are then transferred to the enzyme CoA to produce Acetyl CoA. The hydroxyethyl group is oxidized to an acetyl group and the electrons are picked up by NAD forming NADH.
The oxidized carboxyl group is converted to CO2 which is released o 2 remaining carbon molecules are oxidized into acetate. Pyruvate Oxidation In the presence of oxygen pyruvate is transformed into an acetyl group attached to a carrier molecule of coenzyme A. O Acetyl-CoA is the first substrate in the citric acid cycle.
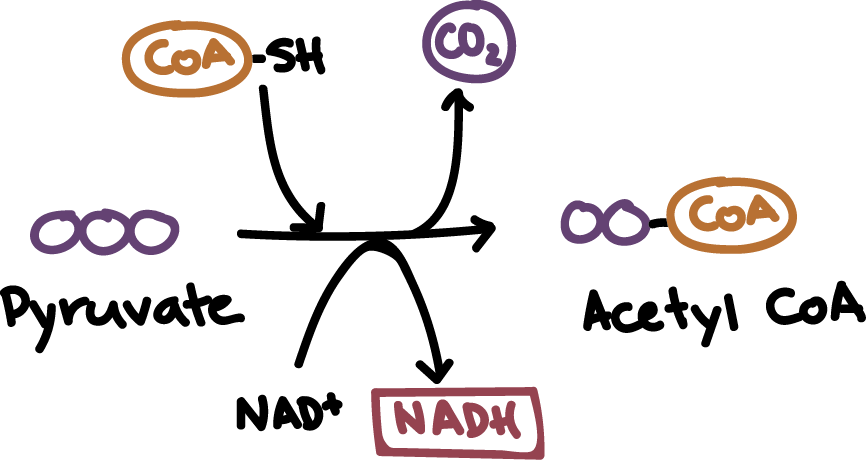
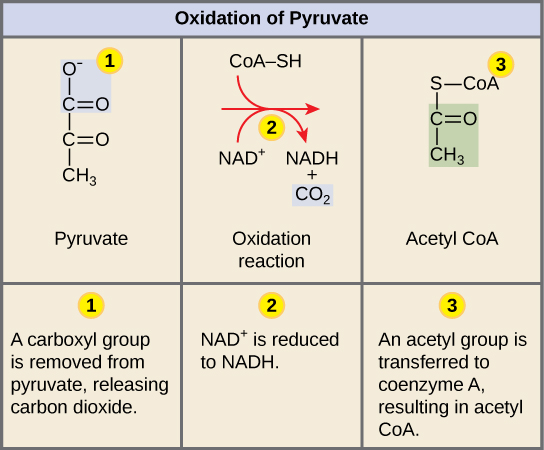
The high-energy electrons from NADH will be used later to generate TPA. There an enzyme system called the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is responsible for the conversion of pyruvate to carbon dioxide and the acetyl portion of acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate oxidation steps A carboxyl group is removed from pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide.
List the products of the citric acid cycle. As a result CoA is frequently shown in equations as CoA-SH. The oxidized two-carbon molecule an acetyl group is attached to Coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA.
There pyruvate will be transformed into an acetyl group that will be picked up and activated by a carrier compound called coenzyme A CoA. Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA what molecules are produced and how it links glycolysis to the Krebs cycle. Describe the point at which glucose is completely oxidized during cellular respiration.
Note the role of oxaloacetate in this cycle. Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis which is converted into acetyl coA that enters the Krebs cycle when there is sufficient oxygen available. For each mole of acetyl CoA oxidized in this pathway there is a yield of.
Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl CoA what molecules are produced and how this process links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. This pathway is sometimes known as the Krebs cycle after its discoverer Sir Hans Krebs. Pyruvate is oxidized in a reaction that generates acetyl CoA NADH and CO2Figure 3.
Pdh pyruvate dehydrogenase key regulatory step - irreversible reaction converts pyruvate sugar to either fatty acid or completely oxidized to co2 allosteric regulation of pdh complex if cell has high energy levels pyruvate is not converted to acetyl - coa so high energy molecules nadh atp acetyl - coa act as allosteric. Describe the form and fate of the carbons in the Krebs cycle. Jun 4 2013 921 am -0500.
Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA what molecules are produced and how it links glycolysis to the Krebs cycle. The resulting compound is called acetyl CoA. Explain why it is called a cycle.
There pyruvate will be transformed into an acetyl group that will be picked up and activated by a carrier compound called coenzyme A CoA. This preview shows page 8 - 10 out of 26 pages. Explain how the slide of electrons down the electron transport chain is coupled to the production of ATP by chemiosmosis.
The reaction is catalysed by the multi-enzyme complex consisting of several different enzymes. The acetyl group is picked up by a carrier compound called coenzyme A CoA which is made from vitamin B5. Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl CoA what molecules are produced and how this process links glycolysis to the krebs cycle.
During glycolysis glucose is broken down into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. How pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to acetyl CoA so it can enter the citric acid cycle. In the presence of oxygen pyruvate enters the remaining stages of cellular respiration.
The resulting acetyl CoA can enter several pathways but most often the acetyl group is delivered. CoA is made from vitamin. O Pyruvate is decarboxylated.
Distinguish between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition 12. There is an SH group at one end of the CoA molecule which is the point at which the acetyl group is attached. The mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex then catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to produce acetyl-CoA a two-carbon acetyl unit.
Acetyl CoA can be used in a variety of ways by the cell but its major function is to deliver the acetyl group derived from pyruvate to the next pathway in glucose catabolism. In eukaryotic cells the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria which are the sites of cellular respiration. Pyruvate is decarboxylated in the presence of thiamine pyrophosphate.
Acetyl CoA is further oxidized to CO2and H2O in the citric acid cycle described in detail below. The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is a three-step process. O Coenzyme A attaches to the acetate forming Acetyl-CoA.
The resulting compound is called acetyl CoA. The e-s are stored temporarily in coenzyme NAD NADH after reduction. Pyruvate oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl-CoA active acetate before entering the citric acid cycle.
CoA is made from vitamin B5 pantothenic. Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl CoA and how this reaction links to the Krebs cycle. The resulting compound is called acetyl CoA Figure 2.
Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl CoA what molecules are produced and how this process links glycolysis to the Krebs cycle. In the presence of oxygen acetyl CoA delivers its acetyl 2C group to a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate to form citrate a six-carbon molecule with three carboxyl groups. This single pathway is called by different names.
The resulting compound is called acetyl CoA. When the oxygen is insufficient pyruvate is broken down anaerobically creating lactate in animals including humans and ethanol in plants. There pyruvate is transformed into an acetyl group that will be picked up and activated by a carrier compound called coenzyme A CoA.
Pyruvate is modified by removal of a carboxyl group followed by oxidation and then attached to Coenzyme A. In eukaryotic cells the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into the mitochondria which are the sites of cellular respiration. This is the currently selected item.
Carried out by a multi enzyme complex that catalyzes 3 reactions. The two-carbon molecule from the first step is oxidized and NAD accepts the electrons to form NADH. The acetate of acetyl CoA undergoes a stepwise oxidation to carbon dioxide and water in a cyclic pathway the citric acid cycle shown in Figures 517 and 518.
In eukaryotic cells the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria which are the sites of cellular respiration. This complex is known as pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.

Oxidation Of Pyruvate And The Citric Acid Cycle Boundless Biology
Pyruvate Oxidation Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy
Pyruvate Oxidation Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy
0 Response to "Describe Where Pyruvate Is Oxidized to Acetyl Coa"
Post a Comment